The first year of interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve-- the Prospect of G7 and RMB Exchange rate in 2022. For more information on export to China, please call SINOLOBEN, service Email: sinoloben@sloben.com.
In 2021, the global economy will still be plagued by the COVID-19 epidemic. The
continuous variation of the virus has kept the epidemic in a phased
outbreak, while the uneven distribution of vaccines has also affected
some developing countries, disrupting global supply chains, soaring raw
material prices and thwarting economic recovery. Against
the backdrop of high inflation, the Fed began to shift its loose
monetary policy from June. The Fed officially began to scale back its
bond purchases in November, announced an accelerated narrowing in
December, and expected to raise interest rates three times in 2022. Under the dual logic of risk aversion and monetary policy differentiation, the dollar strengthened across the board in 2021.
Although
new mutations may still occur in novel coronavirus in 2022, the impact
of the epidemic on economic activity is expected to diminish, given the
increased popularity of vaccines in developing countries and the
acceleration of vaccination in developed countries. Under
the assumption that the impact of the epidemic is gradually weakening,
global economic demand is expected to return to the upward track, and
changes in monetary policy may become the main line of foreign exchange
market transactions in 2022. Among them, the Fed's policy is undoubtedly the top priority. Based
on the Fed's latest bitmap and projections of the trading level of the
interest rate derivatives market, we expect the Fed to start raising
interest rates in the second quarter of 2022.
Under
our baseline assumption, the exchange rate market in 2022 is expected
to take the start of the Fed rate hike cycle as a turning point. We
expect the dollar index to continue to appreciate in the first half of
2022 and break through 2021 highs, but after the start of the interest
rate hike cycle, the dollar index may change from rising to falling and
fall back below 95 in the second half of the year. The hub of the euro
against the dollar is expected to recover to 1.14. Historical
experience is basically consistent with our judgment. In the past four
Fed rate hikes, the dollar index tends to rise within six months before
the rate hike and fall within six months after the rate hike. It
is somewhat surprising that the Japanese yen is the major currency with
the largest average increase in the six months after the start of the
Fed's interest rate hike, and can rise by about 10% against the US
dollar on average after raising interest rates. This
is contrary to the current logic of the market that the Fed's interest
rate hike has led to a widening of the spread between Japanese and US
interest rates and the depreciation of the yen. We
believe that it is precisely because the market bears on the yen are
too consistent that the bears of the yen will accumulate before the Fed
raises interest rates, and under the influence of the effect of "buying
expectations and selling facts", the start of the Fed raising interest
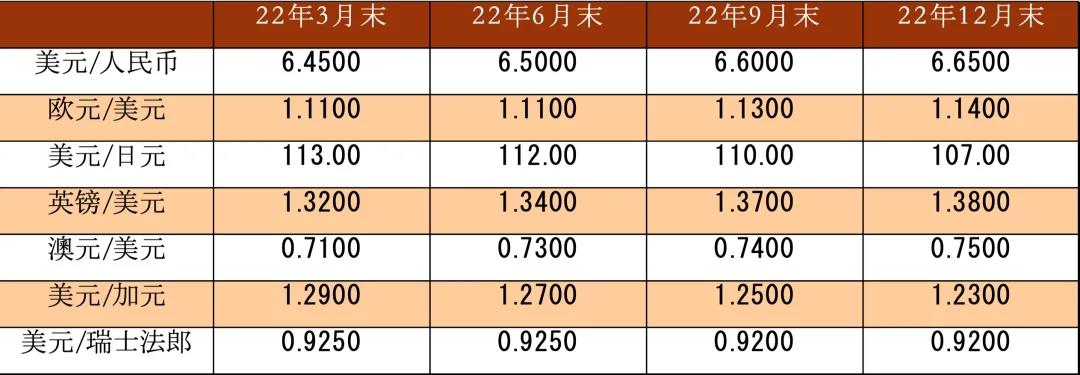
rates has become an opportunity for yen bears to settle. We expect the yen to rebound to 107 by the end of 2022, which is stronger than the market consensus.
The
bilateral exchange rate appreciation of the RMB against the US dollar
against the backdrop of the overall rise in the US dollar index in 2021
has pushed the CFETS index, which measures the rise and fall of the
renminbi against a basket of currencies, to its highest level since the
exchange rate reform in 2015, and the real effective exchange rate index
calculated by the Bank for International Settlements hit an all-time
high in November. Strong epidemic control
has enabled Chinese export manufacturing companies to reap huge
dividends in 2021, when the global supply chain has been devastated by
the epidemic. The 30% increase in exports
has brought a large amount of demand for foreign exchange settlement,
which is the main reason for the RMB to rise against the trend and move
out of the independent market in 2021. In
2022, our baseline assumption is that the impact of the epidemic is
gradually weakening, and the high growth of China's exports is difficult
to sustain in an environment where global monetary policy tends to
tighten. Once export growth slows down, there is a need to repair the valuation of the RMB effective exchange rate. We expect a moderate correction of the RMB in 2022, which will be around 6.65 by the end of the year.
Among
the remaining G7 currencies, we expect the sterling and Canadian
dollars to reach around 1.38 and 1.23 respectively by the end of 2022,
as both the Bank of England and the Bank of Canada have strong
expectations of raising interest rates in 2022. There
is a divergence in monetary policy between the Australian Federal
Reserve and the Federal Reserve in the first half of 2022, and monetary
policy may converge in the second half of the year. We expect the
exchange rate of the Australian dollar to be 0.75 by the end of 2022. Finally,
the Swiss franc, together with the euro, is expected to strengthen in
the second half of 2022, and we expect the US dollar and Swiss franc to
be 0.92 by the end of 2022.